
MRI scanners use very strong magnets to look at the brain by using the “excitability” of the water molecules in our bodies. In addition to CT scans, another imaging technology called magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) can also be used to look inside the brain. Radiology has even gone so far as to engineer what are called “low dose” CT scanners, used most often at children’s hospitals, to try to reduce the amount of radiation young patients are exposed to. While both the X-ray and CT can collect images in a matter of seconds, both techniques use radiation, and repeated radiation exposure can increase one’s risk of various cancers.
The main difference between CT and X-ray is that X-ray just creates a single, two-dimensional image, similar to a picture you would take with your cell phone. All of these signals are collected by a computer, which reconstructs them to form a three-dimensional image of the brain that the radiologist can analyze on a computer to look for injuries. The CT technology uses small bursts of radiation that pass through the body, similar to X-rays, and create different signals depending on the type of tissue they pass through, be it skin, bone, brain, or other tissue types. The CT scanner, as it is known for short, is a machine that allows doctors to see into a patient’s brain without surgery.

When a patient has a brain injury, one of the first things radiologists do in the emergency department of the hospital is to use a special kind of “camera,” called a computed tomography (CT) scanner, to look at the patient’s brain.
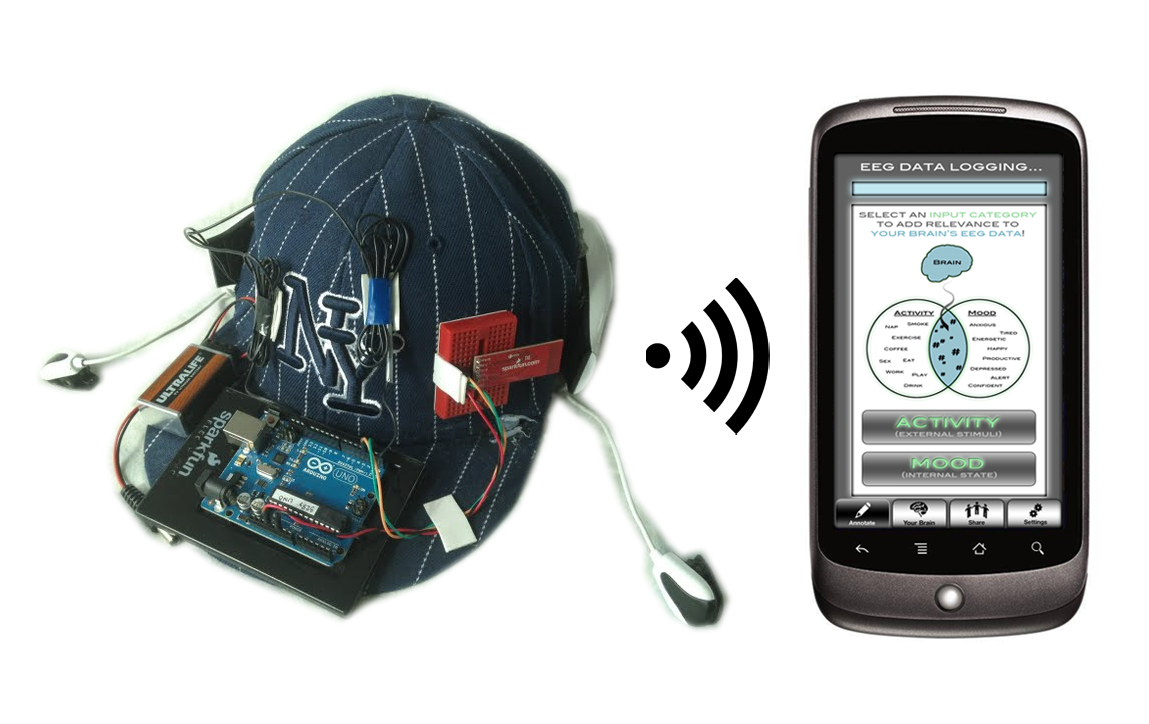


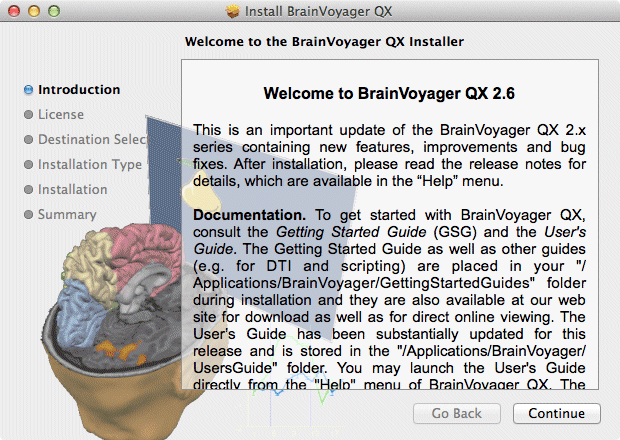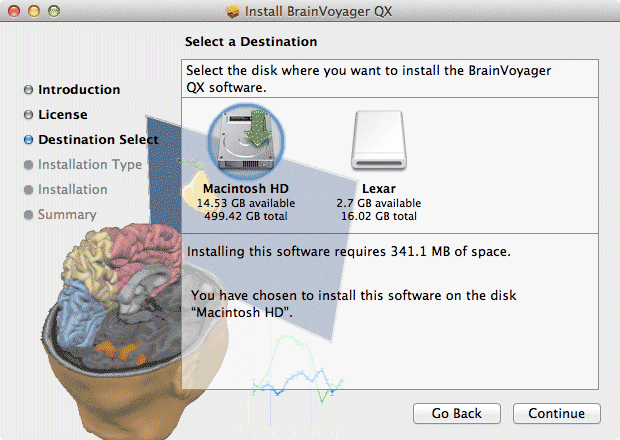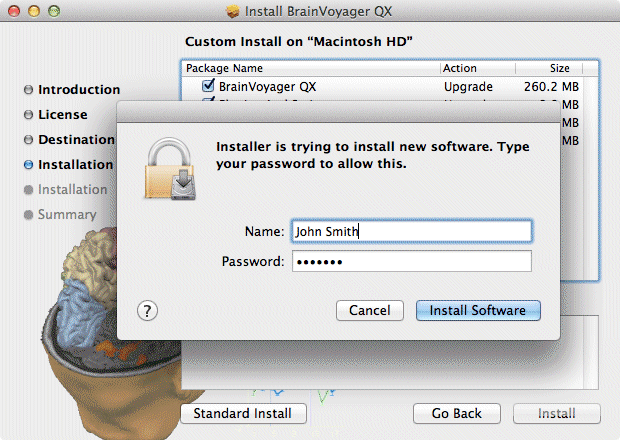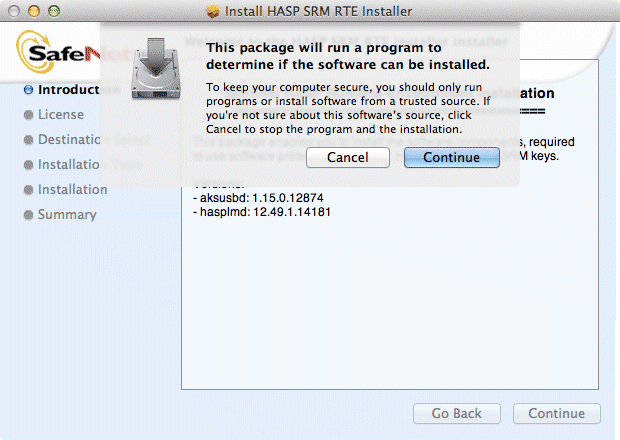
BRAIN SYNC SOFTWARE FOR MAC HOW TO
Did you know that doctors look at the brains of thousands of people every day? In hospitals all over the nation, we are looking into patients’ brains to see if something has gone wrong, so we can understand how to help treat each patient’s condition.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
